Carol Murphy
Research Director, BRI-FORTH, Ioannina
Vasculogenesis, is a fundamental developmental process, during which mesodermal progenitors are differentiated to endothelial cells (ECs). The initial vessel plexus, formed from ECs only, further matures via the process of vascular myogenesis, during which mural cells (MCs), such as pericytes (PCs) and vascular smooth muscle cells (vSMCs), are recruited to the vessels via cross-talk with ECs differentiating locally. Such mature vessels consisting from ECs and PCs/SMCs can form new vessels using spouting in a process called angiogenesis. Many molecules participate in regulating vessel morphogenesis during early development (vasculogenesis) or at later stages of development and postnatally (angiogenesis). Interestingly, VEGFA appears to regulate both processes though in vasculogenesis it achieves the differentiation of mesodermal to vascular progenitor cells (VPCs) and further to ECs whereas in angiogenesis it generates new vessels by sprouting of ECs. Thus, VEGF signalling generates the excessive angiogenesis seen in angiogenic diseases and particularly in tumours. Likewise, VEGF cascades are required for the vasculogenic vessel engineering in Regenerative Medicine. Therefore, a detailed knowledge of VEGF signalling that regulates both angiogenesis and vasculogenesis is needed. However, at present there is almost no information about the vasculogenic VEGF cascades.
Vessel engineering is critical for the success of RM because the speed by which the inoculated cells are vascularised by the host is important. Delayed vascularisation of the implant results in low cell survival rates. Thus, ideally the tissue engineered construct (TEC) should be already vascularised in vitro prior to implantation in vivo. We have already initiated a programme for vessel engineering based on reprogramming human fibroblasts to generate human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) and subsequent differentiation of hiPSCs, via mesodermal intermediates, to VPCs and then to ECs in chemically defined media (CDM) or to PCs/vSMCs. Whereas this is a step forward, there are many gaps in our knowledge that need to be addressed. Indeed, the mesodermal VEGFR2+ intermediate cell populations and VPCs are not well characterised and almost nothing is known about the VEGF-A-induced signalling cascades that differentiate/commit mesodermal intermediates to VPCs and then to ECs. Using a combination of cutting-edge technologies, we will explore the signalling pathways of VEGF-A responsible for vasculogenesis, the de novo emergence of endothelial cells from mesoderm (see aims).
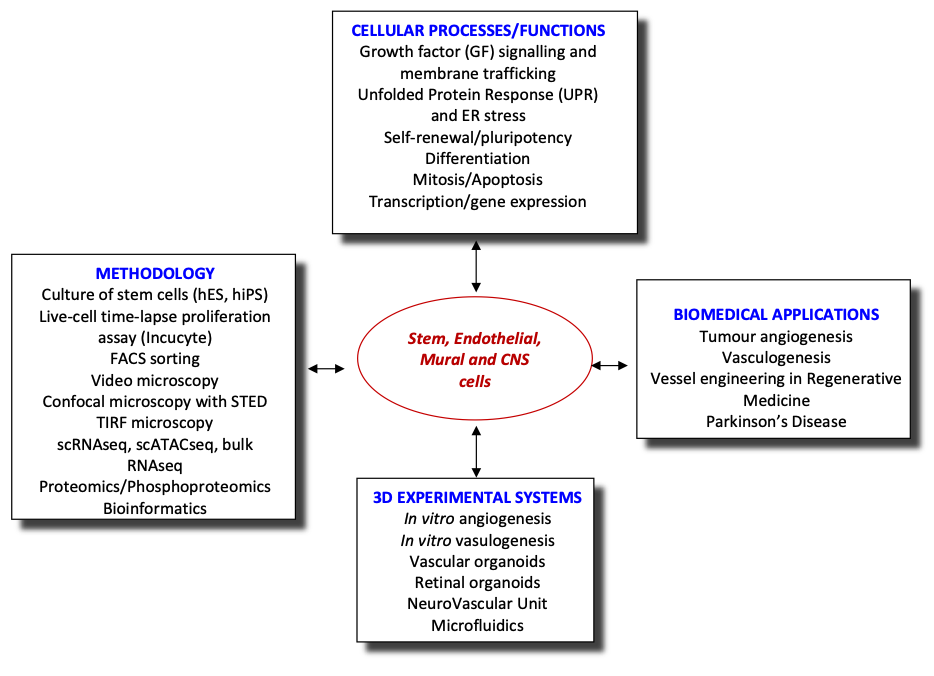
Recently, we have extended our research into the role of endothelial cells in neurodegenerative diseases, using Parkinson’s Disease as a model system. We are establishing a PD NeuroVascular Unit combining all relevant cells (astrocytes, microglia, dopaminergic neurons, endothelial cells and pericytes) in a microfluidic platform to investigate the cell-cell communication and alterations in this system. Additionally, this system will be used for preclinical studies on treatments for PD.
Aims
- Determining the VEGF-induced circuit regulating vasculogenesis during vessel engineering by employing phosphoproteomics, single cell RNAseq, single cell ATACseq and bioinformatics.
- Evaluating the involvement of flow/shear stress and Mural cells in the differentiation of hiPSCs to ECs via mesodermal intermediates in microfluidic platforms.
- Establishing a preclinical model of PD using human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) from PD patients and isogenic controls to investigate the NeuroVascular Unit in PD.








